Plan for Soil Instrumentation and Equipment in Urban Greening Projects
The configuration plan for soil instrumentation and equipment in urban greening projects should cover multiple stages, including soil sampling, pretreatment, analysis and testing, and data management, to ensure effective monitoring and management of soil quality. Below is a comprehensive configuration plan:

Soil Sampler: Used to collect soil samples from different depths and layers in urban green areas for subsequent analysis. Both manual and power-driven samplers can be selected based on actual needs.
Soil Sieve/Soil Sifter: Used to screen soil particles of different sizes to obtain uniform soil samples for further analysis.
2. Soil Pretreatment Equipment
Soil Grinder: Grinds soil samples to an appropriate fineness for subsequent chemical analysis or physical property testing.
Electric Thermostatic Blow-Drying Oven: Used for drying soil samples to ensure they are in a dry state before testing, avoiding the impact of moisture on test results.
Electronic Balance: Used for accurately weighing soil and reagents to ensure the precision of experimental data.
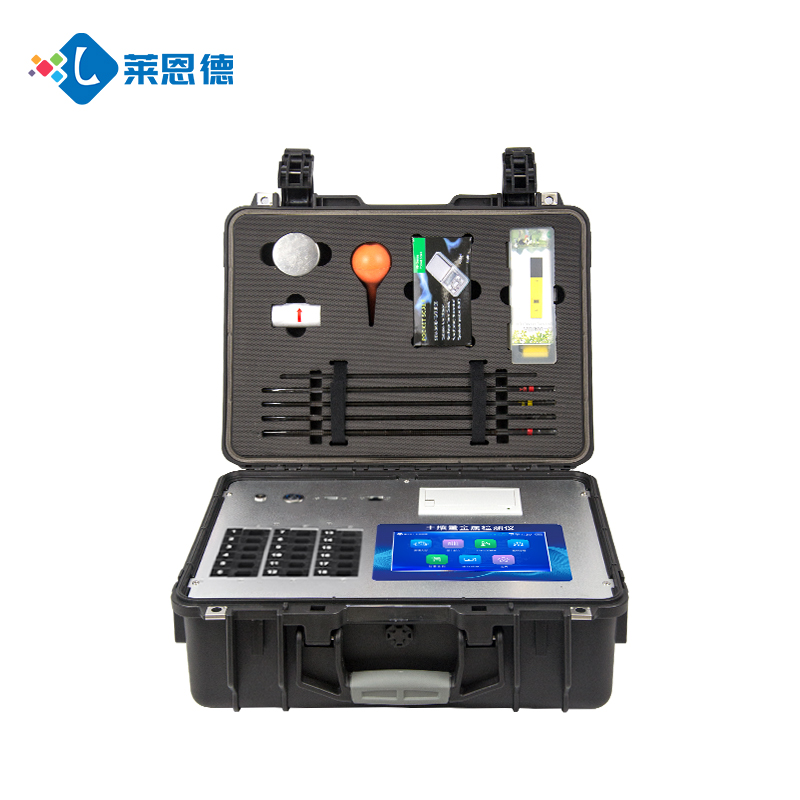

3. Soil Analysis and Testing Equipment
Soil Nutrient Rapid Tester: Quickly measures the content of major nutrients such as nitrogen, phosphorus, and potassium in the soil, as well as indicators like organic matter and pH. This is crucial for assessing soil fertility and formulating fertilization plans.
pH Meter: Measures the acidity and alkalinity of the soil to evaluate soil fertility and plant growth conditions. Different plants have varying adaptability to soil pH, so measuring pH is essential for selecting suitable plant species and developing soil improvement measures.
Conductivity Meter: Measures the electrical conductivity of the soil solution, reflecting the salt content. High salt content may adversely affect plant growth, so measuring conductivity helps detect and address soil salinity issues in a timely manner.
Atomic Absorption Spectrophotometer: Used to measure the content of trace elements in the soil, such as zinc, copper, iron, and manganese. These trace elements play an important role in plant growth and development, so their measurement is vital for developing scientific fertilization plans.
4. Data Management Equipment
Computer and Data Processing Software: Used for storing, analyzing, and processing experimental data, as well as generating reports and charts. This helps managers intuitively understand soil quality conditions and develop targeted management measures.
Printer: Used for printing experimental reports and charts, facilitating record-keeping and archiving.
5. Other Auxiliary Equipment
Laboratory Pure Water System: Provides high-quality pure water to meet the high standards required for experiments.
Laboratory Safety Equipment: Such as personal protective equipment like safety goggles, gloves, and masks, as well as safety facilities like fire extinguishers and emergency showers, to ensure the safety of laboratory personnel.
Laboratory Furniture and Facilities: Such as laboratory benches, cabinets, and fume hoods, to provide necessary workspace and storage for experiments.
In summary, the configuration plan for soil instrumentation and equipment in urban greening projects should cover multiple stages, including soil sampling, pretreatment, analysis and testing, and data management, to ensure effective monitoring and management of soil quality. Depending on actual needs and budget constraints, the types and quantities of equipment in the configuration plan can be flexibly adjusted.