Make Diseased Meat Nowhere to Hide! Practical Guide to Lanende Diseased Meat Detector
With the advancement of technology, consumer demands are also continuously evolving. More and more people are paying attention to the source and quality of food, imposing higher standards for meat safety. In this context, promoting and using the Lanende Diseased Meat Detector has become particularly important. When the detector malfunctions, timely and effective responses are crucial. Below is a comprehensive guide for using the Lanende Diseased Meat Detector, especially when troubleshooting issues:

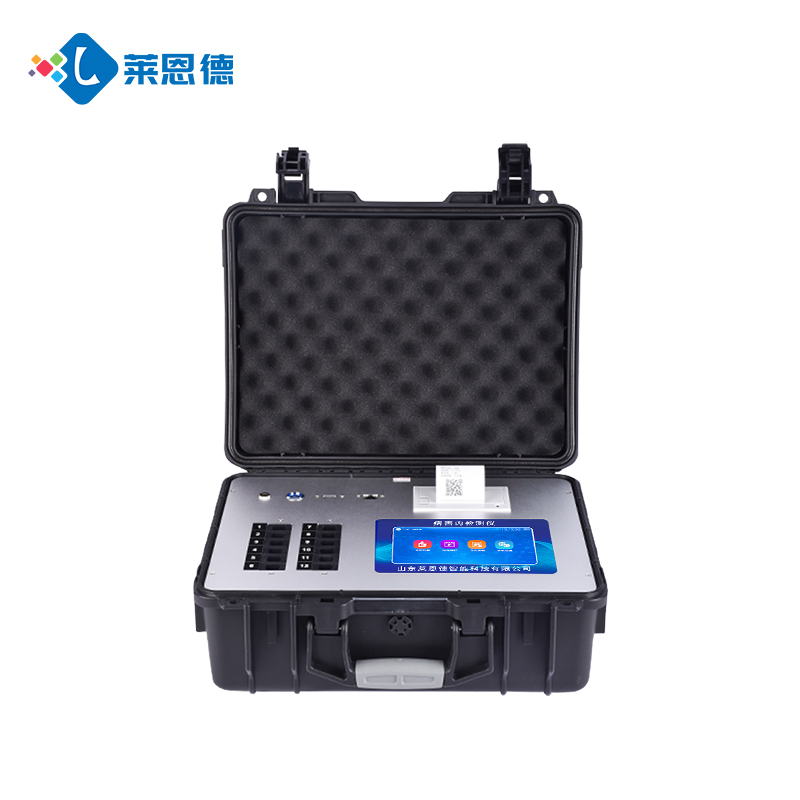
I. Fault Identification and Preliminary Handling
Observe the Fault Phenomenon:
Carefully observe the error messages or abnormal behaviors displayed by the instrument, such as error codes, unresponsiveness, or abnormal detection results.
Consult the Manual:
Refer to the user manual or operation guide provided with the instrument to find explanations and solutions related to the observed fault.
Power Cycle:
Try turning off the instrument’s power, wait a few seconds, and then restart it to resolve minor software or system lag issues.

II. Common Faults and Handling Methods
Error Codes:
If error codes (e.g., F0001) appear, refer to the error code table in the manual to identify the specific cause.
F0001 typically indicates an overcurrent fault, which may be caused by excessive load, motor failure, power supply issues, or sensor damage.
Solutions include checking whether the load is within the design range, inspecting the motor’s condition, ensuring stable power supply voltage, and checking for sensor damage.
No Display or Unresponsive Buttons:
Check if the power supply is properly connected and try using a different power outlet or cable.
Inspect the instrument for loose or damaged internal components. If necessary, contact a professional for repairs.
Abnormal Detection Results:
Ensure that reagents are within their validity period and correctly prepared.
Check whether sample handling complies with specifications to avoid cross-contamination.
Retry the detection to eliminate random errors.
III. Professional Repair and Technical Support
Contact the Manufacturer or After-Sales Service:
If the fault cannot be resolved independently, promptly contact the instrument manufacturer or after-sales service center for professional repair and technical support.
Provide Detailed Information:
When contacting the manufacturer or after-sales service, provide detailed information such as the instrument model, fault phenomena, and attempted troubleshooting steps to help them diagnose the issue more quickly.
Follow Repair Recommendations:
Adhere to the repair or part replacement recommendations provided by the manufacturer or after-sales service.
IV. Usage and Maintenance Recommendations
Regular Calibration:
Calibrate the instrument periodically to ensure its accuracy and stability.
Cleaning and Maintenance:
Clean the instrument promptly after use to avoid damage from residue.
Perform regular maintenance, such as replacing filter paper or cleaning optical components.
Standardized Operation:
Follow the instrument’s operation guidelines and adhere to standardized procedures to avoid malfunctions caused by improper operation.
Maintain Usage Logs:
Keep records of the instrument’s usage, detection results, and maintenance history for future analysis and reference.
In summary, when the Lanende Diseased Meat Detector malfunctions, initial steps such as observing the fault, consulting the manual, and power cycling should be taken first. If the issue persists, contact the manufacturer or after-sales service promptly for professional repair and technical support. Additionally, regular calibration, cleaning, maintenance, and standardized operation should be emphasized during daily use to ensure the instrument’s accuracy and reliability.
 PrevLanende Intelligent Pesticide Residue Rapid Detector: A Fast and Accurate Tool for Pesticide Residue Detection
PrevLanende Intelligent Pesticide Residue Rapid Detector: A Fast and Accurate Tool for Pesticide Residue Detection NextPortable Water Quality Aquaculture Detector: Easily Monitor Water Conditions for Smarter Aquaculture Management.
NextPortable Water Quality Aquaculture Detector: Easily Monitor Water Conditions for Smarter Aquaculture Management.
Recent Articles

Lanende’s Ultrasonic Cell Disruptor Powers Cross‑Industry Innovation with Precise, Efficient Sample Processing

Lanende Launches Fully Automated Closed‑Cup Flash Point Meter, Marking New Milestone in Safety Analysis Capabilities

Lanende Launches Split-Type Ultrasonic Cell Disruptor – Empowering Life Science Research and Industrialization with Precision